by Stephanie Dunn
February 26, 2016
As organizations continue to grow, corporate mergers and partnerships with other organizations can face security challenges in establishing trust relationships to connect various domains and network resources together. Establishing trust relationships provides flexibility in allowing users and groups to access data their data from any location within an organization. Organizations that do not continuously monitor network endpoints could increase the potential of attackers gaining access to other domains and hosts by exploiting trust relationships. This dashboard aligns with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) ID.AM-3 and PT.PT-3 subcategories that allow an organization to monitor and control access to internal trust connections.
The CSF provides guidance based on existing standards, guidelines, and practices that can be tailored to specific organizational needs. The CSF Protect category is divided into multiple subcategories that address specific security requirements with Access Control, Awareness, Data Security, Policies and Procedures, Maintenance, and Technology Protection. Within the CSF Identify category, specific security requirements are addressed for Asset Management, Business Objectives, and Regulatory policies. Together, the Protect and Identify categories can assist organizations in achieving business purposes by managing and monitoring the security of trust relationships.
This dashboard can assist the organization in providing details on established trust relationships, internal, and external network connections, and monitoring group and user changes. The Nessus Network Monitor (NNM) will analyze data on established client and server relationships on the network. Several components within this dashboard detect trusted internal connections over ports, protocols, and services, as well as traffic over suspicious ports. Traffic between internal and external network connections will display information on internal hosts traffic, which will allow the analyst to detect any suspicious or unauthorized host connections. The Log Correlation Engine (LCE) will detect changes in trust relationships such as existing trusted hosts, new trust relationships, forest trust changes, and trusted logons. Changes among new users and group memberships can uncover unauthorized accounts with administrative privileges that could exploit trust relationships.
Managing trust relationships requires continuous monitoring across every domain within an organization. Trust relationships are established connections between servers, workstations, forests and domains allowing for interoperability across network resources. However, trust relationships can also be exploited. Attackers who gain administrative privileges on one domain can obtain access to resources on other trusted domains and hosts. Ports can also be compromised through trust relationships between internal and external firewalls. Detecting for changes in internal and external network traffic patterns could indicate the presence of malicious activity, and should be investigated further.
The dashboard and its components are available in the Tenable.sc Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Tenable.sc Feed under the category Compliance & Configuration Assessment. The dashboard requirements are:
- Tenable.sc 5.2.0
- Nessus 8.9.0
- LCE 6.0.0
- NNM 5.9.0
Tenable.sc Continuous View (CV) is the market-defining continuous network monitoring platform. Tenable.sc CV includes active vulnerability detection with Nessus and passive vulnerability detection with Tenable’s Nessus Network Monitor (NNM), as well as log correlation with Tenable’s Log Correlation Engine (LCE). Using Tenable.sc CV, an organization will obtain the most comprehensive and integrated view of its trust relationships across an organization.
This dashboard contains the following components:
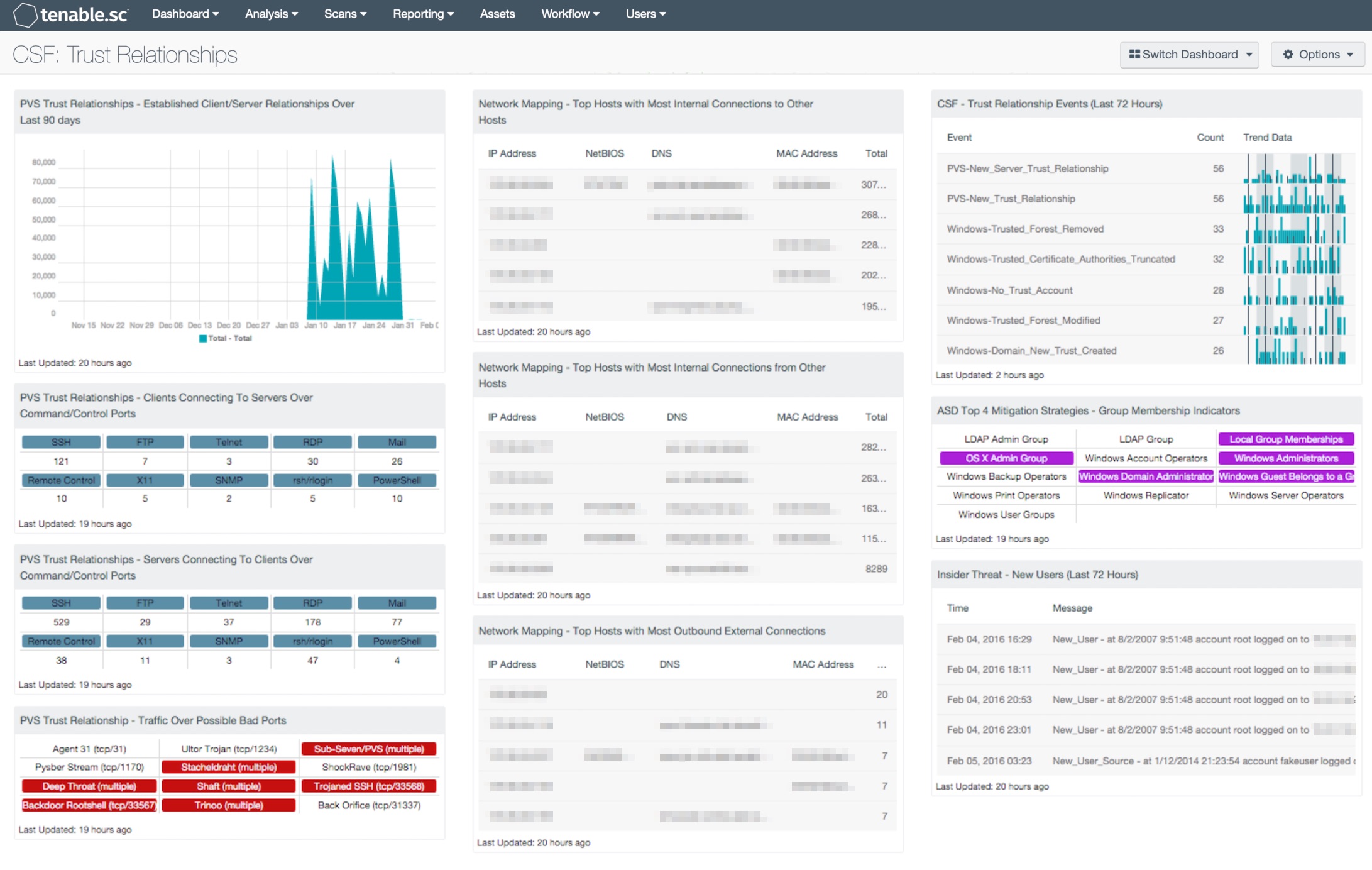
- NNM Trust Relationships - Established Client/Server Relationships Over Last 90 days: This trend component graphs data on internal client trusted client and server connections over a 90 day period. The Passive Vulnerability Scanner can detect both internal clients and servers that a host has connected to on a particular port. The connections displayed within this chart are considered “trusted” relationships within the monitored network range.
- NNM Trust Relationships - Clients Connecting To Servers Over Command/Control Ports: This component collects data on internal trusted client connections. Results are sorted by TCP port and displayed in a series of matrix indicators within the individual component. Some of the most common ports, services, and protocols are included within this matrix. This information can help organizations determine whether any unauthorized or suspicious host connections.
- NNM Trust Relationships - Servers Connecting To Clients Over Command/Control Ports: This component collects data on internal trusted client connections. Results are sorted by TCP port and displayed in a series of matrix indicators within the individual component. Some of the most common ports, services, and protocols are included within this matrix. This information can help organizations determine whether any unauthorized ports or services are in use, as well as any suspicious host connections.
- NNM Trust Relationship - Traffic Over Possible Bad Ports: This component collects data on internal client trusted client connections. Results are sorted by TCP port and displayed in a series of matrix indicators within the individual component based on the TCP ports of common malware that are known to establish command and control sessions between hosts. Organizations can use this information to identify and block potential entry points for malicious activity.
- Network Mapping - Top Hosts with Most Internal Connections from Other Hosts: This table presents information on those hosts with the most passively detected internal connections from other hosts (Internal Server Trusted Connection). The table is sorted so that the host with the highest count of detections is at the top. This information can assist an organization in understanding who is talking to whom, as well as detecting any unauthorized or suspicious host connections. The Total column displays the number of detections. This number of detections may not equal the number of other hosts connecting to this host, as some detections may include multiple hosts, and multiple connections from the same host may also have been detected. Note that only passively detected internal host connections will be displayed, and this may not include all possible internal connections.
- Network Mapping - Top Hosts with Most Outbound External Connections: This table presents information on those hosts with the most passively detected outbound external connections. The table is sorted so that the host with the highest count of detections is at the top. This information can assist an organization in understanding who is talking to whom, as well as detecting any unauthorized or suspicious host connections. The Total column displays the number of detections. This number of detections may be greater than the number of external hosts to which this host is connecting, as multiple connections to the same host may have been detected. Note that only passively detected outbound external host connections will be displayed, and this may not include all possible external connections.
- CSF – Trust Relationships Events (Last 72 Hours): This component displays detected trust relationship event changes within the last 72 hours. Trust relationships are used to establish a trusted connection between domains and hosts. This can allow for users in one domain to connect to resources in another trusted domain. Workstations that have joined to a domain controller also have an established trust relationship. The events are detected by the Nessus Network Monitor (NNM), and then forwarded to the Log Correlation Engine (LCE). The component table is sorted by the highest number of events at the top, and leverages several normalized event types that will detect changes in trust relationships on a network. Events displayed in this table can assist the analyst in obtaining information on trusted connections, failed connections, and modifications of trusted relationships.
- ASD Top 4 Mitigation Strategies - Group Membership Indicators: This Group Membership component is a matrix of saved queries which quickly identifies plugins that match on group membership settings. When a query result is greater than 1, the indicator will turn purple. Plugin ID 45477 defines LDAP Group indicators as a query in remote LDAP for a list of groups. Plugin 71246 connects to a host via SMB and retrieves a list of local Groups and their Members. Plugin 10901 collects the members of the Account Operators group. Members of this group can create or modify local user accounts but cannot modify or create administrative accounts or edit user rights. These are just a few of the indicators in this matrix.
- Insider Threat - New Users (Last 72 Hours): This table presents new user events recorded in the last 72 hours. The raw syslog of the event is given, displaying the event, the user account, and the host IP address. The 'New network user' event records the first time a user is ever seen on the network. The 'New_User' event records the first time a user logs in to a new host and/or a new account type on a host. The 'New_User_Source' event records the first time a user logs in from a new host. All of these new users should be verified as authorized to be on the network and accessing the systems that they are accessing.