by Cody Dumont
August 21, 2014
Log management is a problem that many organizations face on a regular basis. This dashboard provides a summary of log sources, and monitors audit checks for Network Time Protocol (NTP) settings.
The dashboard and its components are available in the SecurityCenter Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, assurance report cards and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the SecurityCenter Feed under the category Discovery & Detection.
The dashboard requirements are:
- SecurityCenter 4.8.1
- Nessus 5.2.7
- LCE 4.2.2
- Tenable LCE Client
The first step in a successful log management program is to set a standardized time source on the network. Utilizing a Windows Domain Controller as a NTP server is one common practice. While some organizations synchronize with a known, reputable, online resource, others obtain an atomic clock or GPS source and run a private NTP server. Using Group Policy or other configuration management tools, the NTP source is set.
Additional steps include the configuration of routers, switches, and other network equipment to forward logs to Log Correlation Engine (LCE). Logging can be enhanced further by deploying the LCE Clients throughout the network. A good practice is to have LCE Clients installed on all servers, and in a best-case scenario all workstations should also have the LCE Client installed. The LCE policies for servers would be more inclusive to capture web server, mail server, or other application logs, while workstation LCE policies can be more limited and only collect malware events and a subset of event logs.
SecurityCenter Continuous View (CV) supports a tight integration with SIEMs, malware defenses, firewalls, network systems, servers, workstations and virtualization systems. The ability of LCE to normalize events from many sources and identify the vulnerabilities is unmatched in the industry. Log normalization is one of the many methods of how Tenable provides continuous network monitoring to identify vulnerabilities, reduce risk, and ensure compliance.
Components
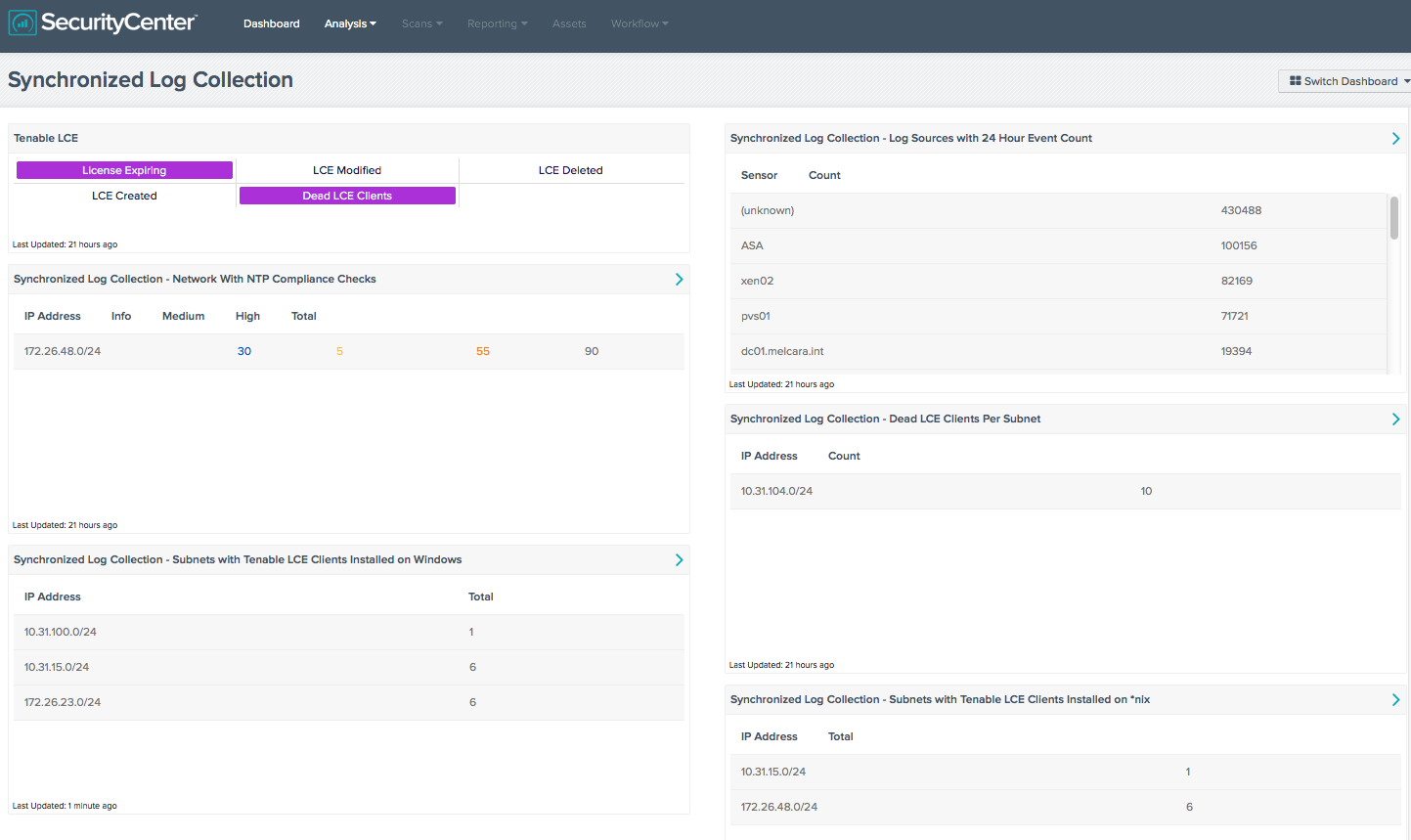
Tenable LCE: This matrix component displays event data related to Tenable's Log Correlation Engine. It includes indicators that trigger if the LCE license is within 5 days of expiration, and if any modifications have occurred to the LCE.
Synchronized Log Collection - Network With NTP Compliance Checks: This component reports on audit checks that verify the NTP settings on subnets. Centralized and time-synchronized logging, and timely log analysis will increase an organization’s ability to rapidly identify patterns of suspicious behavior and correlate logged events across multiple workstations and servers. This practice enables investigation and auditing functions to be easier and more effective should an intrusion occur.
Synchronized Log Collection - Log Sources with 24 Hour Event Count: This component identifies log sources and helps the organization ensure that all systems that can send logs are sending them to LCE and/or allowing PVS to scan them. Identifying patterns of suspicious behavior using PVS, and sending these logs to the LCE, will show correlated events across multiple workstations and servers. This practice enables investigation and auditing functions to be easier and more effective should an intrusion occur. For the sensor (unknown) logs, these are syslogs received from an unknown IP address. To name these devices in LCE 4.2.2 and lower, edit the “/opt/lce/admin/syslog_sensors.txt” file. For users who have installed LCE 4.4, there is a new GUI interface; new sensors can be defined at Configuration > Advanced > Syslog Sensor Names.
Synchronized Log Collection - Subnets with Tenable LCE Clients Installed on Windows: This component displays the number of Windows hosts per subnet on which the LCE Client is installed. Systems without the LCE Client installed do not send their logs to LCE, therefore vulnerabilities on these systems might not be found. System administrators can also monitor the counts per subnet, which provides information on devices that may not be properly monitored by LCE. For example, if each subnet has 100 workstations and the count shows 45, either all systems are not scanned by Nessus or all systems don’t have LCE installed.
Synchronized Log Collection - Dead LCE Clients Per Subnet: This component displays the count of hosts with “dead” (unreachable) LCE Clients per class C subnet. DHCP leases that have expired may cause the number of reported dead LCE clients to increase, as can other events that may trigger a device’s IP address to change. As these numbers fluctuate, administrators should investigate, determine the cause, and validate that systems are still properly being monitored.
Synchronized Log Collection - Subnets with Tenable LCE Clients Installed on *nix: This component displays the number of *nix hosts per subnet on which the LCE Client is installed. Systems without the LCE Client installed do not send their logs to LCE, therefore vulnerabilities on these systems might not be found. System administrators can also monitor the counts per subnet, which provides information on devices that may not be properly monitored by LCE. For example, if each subnet has 100 workstations and the count shows 45, either all systems are not scanned by Nessus or all systems don’t have LCE installed.