사이버 보안 스냅샷: 우리가 무엇을 걱정? 비즈니스가 생성형 AI를 도입하면서 보안 위험 증가

Seduced by generative AI’s potential, organizations plunge ahead overlooking its pitfalls. Plus, check out a common flaw that puts web app data at risk. Also, why many zero day bugs last year were variants of known vulnerabilities. Moreover, find out the current cost of a data breach – ouch! And much more!
Dive into six things that are top of mind for the week ending August 4.
1 – Businesses embrace GenAI, ignore security, compliance risks
When it comes to AI use in the workplace, call 2023 the year of living dangerously.
Seeking transformative benefits, businesses of all sizes and across industries are using generative AI tools like ChatGPT, but most are turning a blind eye to the technology’s risks in areas like cybersecurity and compliance.
That’s according to a McKinsey & Co. survey on the current state of AI. A third of respondents indicated that their organizations are using generative AI regularly for at least one business function – mostly in marketing/sales, product development and service operations.
But most generative AI early adopters are overlooking these tools’ risks. For example, only 21% of surveyed organizations have drawn up policies for employee use of generative AI. Only 38% are actively mitigating cybersecurity risks. The rate is lower for regulatory compliance risks at 28%.
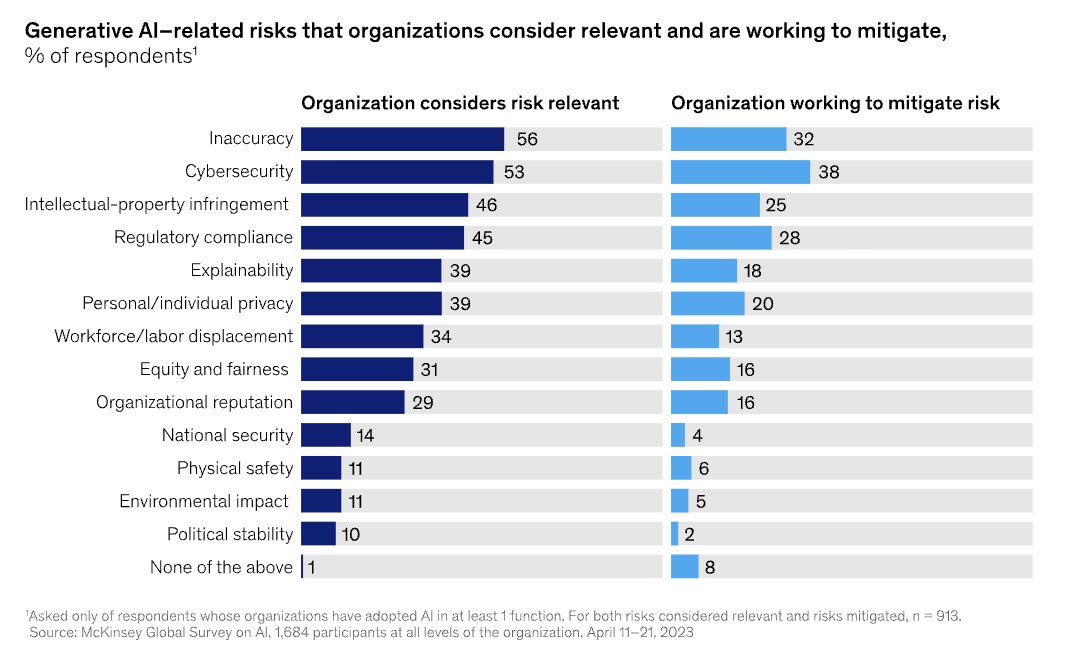
McKinsey & Co. surveyed 1,684 organizations, of which 913 are using AI in at least one business function. Among those using AI, 60% are using generative AI.
To get more details, check out the report, titled “The state of AI in 2023: Generative AI’s breakout year.”
For more information about using generative AI tools securely and responsibly:
- “8 Questions About Using AI Responsibly, Answered” (Harvard Business Review)
- “CSA Offers Guidance on How To Use ChatGPT Securely in Your Org” (Tenable)
- “Responsible AI at Risk: Understanding and Overcoming the Risks of Third-Party AI” (MIT Sloan Management Review)
- “ChatGPT-like Tools Will Boost Developers’ Speed – and Amplify Cyber Risk” (Tenable)
- “How AI ethics is coming to the fore with generative AI” (ComputerWeekly)
2 – Beware a common web app flaw that puts data at risk
U.S. and Australian cyber agencies are warning about a common type of security flaw that malicious actors exploit to tamper with web application data.
Known as insecure direct object reference (IDOR) vulnerabilities, these access-control flaws cause a web app to perform inadequate authentication and authorization checks. When successfully exploited, IDOR flaws allow hackers to modify, delete and access data by sending requests to a website or web API using the identifier of legitimate users.
“These vulnerabilities are frequently exploited by malicious actors in data breach incidents because they are common, hard to prevent outside the development process, and can be abused at scale,” reads the joint advisory from the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC), U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), and U.S. National Security Agency (NSA).

The document describes IDOR vulnerabilities, explains the ways in which they can be exploited and details mitigations for web app vendors, designers, developers and end users.
Recommended mitigations include:
- Vendors, designers and developers should:
- Implement secure-by-design and secure-by-default principles
- Ensure web apps conduct authentication and authorization checks for every request to modify, delete and access data
- Use automated code-review tools to spot and fix IDOR flaws
- Don’t expose IDs, names and keys on URLs, but rather replace them with random values that are cryptographically strong
- End users should:
- Practice security due diligence when evaluating web apps
- Patch web apps as soon as possible
- Do vulnerability scanning and penetration testing on their web apps
To get all the details, read the advisory, titled “Preventing Web Application Access Control Abuse.”
For more information about web app security:
- “Top 10 Web Application Security Risks” (OWASP)
- “Cloud Security Basics: Protecting Your Web Applications” (Tenable)
- “Why API attacks are increasing and how to avoid them” (CSO)
- “Web Application Security: A 2023 Guide” (GBHackers)
- “5 application security threats and how to prevent them” (TechTarget)
VIDEO
How Penetration Testing Helps Secure Web Applications (EC-Council)
Securing Web Apps in Public Clouds (Tenable)
3 – Google: Many zero-day bugs in 2022 were variants of known vulns
In its review of the zero-day vulnerabilities exploited in the wild last year, Google has found that around 40% of them were based on previously reported vulnerabilities. What’s behind this phenomenon?
There are several reasons, including that software makers sometimes don’t fully patch a vulnerability, leaving, for example, its root cause unaddressed, according to Google. This allows savvy attackers to trigger the bug via a different avenue.
“We consider a patch to be complete only when it is both correct and comprehensive. A correct patch is one that fixes a bug with complete accuracy, meaning the patch no longer allows any exploitation of the vulnerability,” reads the report.
Google recommends that software makers do the following when crafting a patch:
- Find the bug’s true root cause, not just the way it was exploited
- Identify additional locations where the bug may exist
- Evaluate other paths that attackers could use to exploit the bug
- Determine if there are any ways around the patch
The report’s other findings include:
- There were 41 zero day bugs exploited in the wild in 2022, down from 69 in 2021
- Of the 41 bugs, 17 were variants of known vulnerabilities
- Android users often had to wait a “significant” amount of time for patches to zero-day bugs
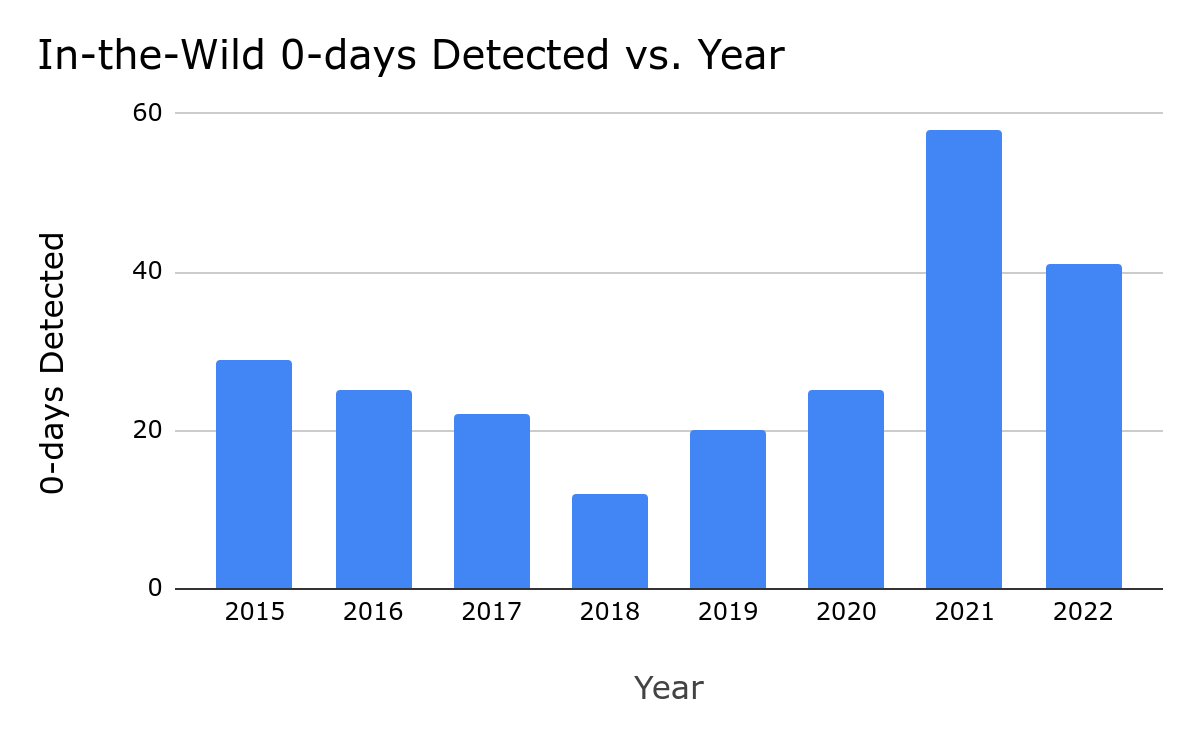
(Source: Google Threat Analysis Group, July 2023)
And speaking of known vulnerabilities, U.S. and international cyber agencies this week published a joint advisory detailing the most commonly exploited vulnerabilities of 2022. The Tenable Security Response Team covered the advisory in-depth in its blog “AA23-215A: 2022's Top Routinely Exploited Vulnerabilities.”
To get more details about the Google findings, check out the full report.
For more information about the topic of faulty software patches:
- “Sloppy Software Patches Are a ‘Disturbing Trend’” (Wired)
- “Zero Day Initiative seeing an increase in failed patches” (TechTarget)
- “Patch Imperfect: Software Fixes Failing to Shut Out Attackers” (Dark Reading)
- “Patch Madness: Vendor Bug Advisories Are Broken, So Broken” (Dark Reading)
4 - IBM: Data breach costs keep rising
A data breach will cost you – a lot. That’s the main finding from IBM’s “Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023,” which pegged the price tag at a global average of $4.45 million – up 15% over three years.
Total Average Cost of a Data Breach (measured in millions of dollars)
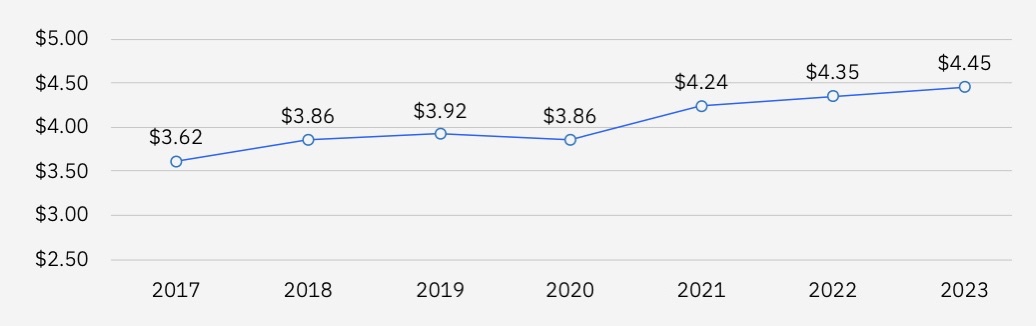
(Source: IBM’s “Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023”, July 2023)
The good news? According to the study, you can reduce the financial hit from a data breach by an average of $1.76 million if you make extensive use of security tools that leverage artificial intelligence and automation. 이유가 무엇입니까?You’ll be able to detect and contain the breach more quickly and effectively.
Moreover, organizations with a mature DevSecOps process for their software development lifecycle also fared better, experiencing an average data-breach cost that was $1.68 million lower than those with less sophisticated DevSecOps processes or with none at all.
Other findings include:
- Among the various breach costs, detection and escalation expenses spiked the most, with a 42% surge, compared with the previous year
- 95% of the organizations analyzed have experienced more than one data breach, but only half of those breached plan to increase their security investments
- The length of a data breach lifecycle was on average 108 days shorter for organizations that use both AI and automation security tools
- Ransomware victims that notified law enforcement saved on average $470,000 in data breach costs, compared to victims that didn’t involve law enforcement
- In 40% of data breaches, attackers compromised data across multiple environments – public cloud, private cloud and on premises
- The average cost a data breach in healthcare skyrocketed to almost $11 million, up 53% since 2020, while critical infrastructure saw a 4.5% jump from last year to $5.04 million
The report, now in its 18th year and conducted by Ponemon Institute, is based on an analysis of real-world data breaches suffered by 553 organizations worldwide from March 2022 to March 2023.
To get more details, check out the report’s home page, a blog about it, the announcement and the 78-page report itself. You can also watch this video:
5 - White House tackles cyber skills shortage
The Biden administration this week launched the National Cyber Workforce and Education Strategy, an initiative aimed at addressing the shortage of qualified cybersecurity professionals in the U.S.
The consensus is that this is a serious problem. There are about 663,000 unfilled cybersecurity jobs in the U.S., which amounts to about a 30% job vacancy rate, according to the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s Cyberseek, which tracks cybersecurity job openings.
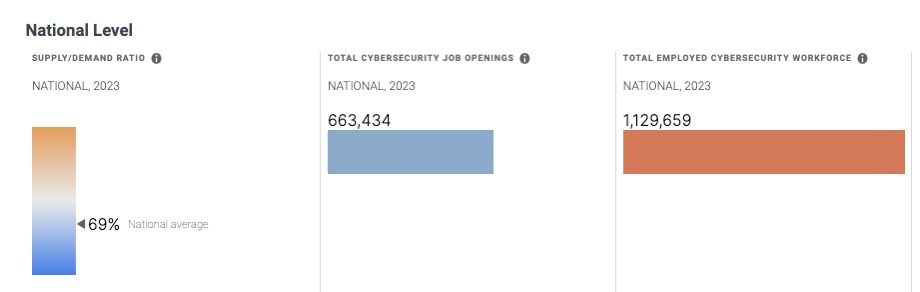
(Source: Cyberseek, Aug. 1, 2023)
The National Cyber Workforce and Education Strategy is founded on four pillars:
- Equip all Americans with foundational cyber skills by offering everybody the opportunity to learn about cybersecurity
- Transform cyber education at all levels, from elementary school all the way to college, including community colleges and technical schools
- Expand and enhance the U.S. cyber workforce by, for example, promoting skills-based hiring
- Strengthen the federal cyber workforce by, for example, lowering barriers associated with hiring and onboarding

Multiple federal agencies are participating in this initiative, as well as private-sector companies, non-profit organizations and educational institutions.
To get more details, read the White House’s announcement, the National Cyber Workforce and Education Strategy’s home page and the 60-page program description.
For more information about the shortage of cybersecurity professionals:
- “12 Ways to Approach the Cybersecurity Skills Gap Challenge in 2023” (InformationWeek)
- “Struggling to fill IT, cybersecurity jobs? Look for non-tech candidates” (Tenable)
- “Cybersecurity skills gap: Why it exists and how to address it” (TechTarget)
- “Hiring entry-level and junior candidates can alleviate the cybersecurity skills shortage” (Tech Republic)
- “The cybersecurity skills gap is a real threat — here's how to address it (World Economic Forum)
6 – A zero trust architecture primer
Looking for an overview of the basics of zero trust? Check out the aptly titled blog “What is a Zero Trust Architecture?” that SANS Institute published this week. It defines what a zero trust architecture is; explains how it’s supposed to work; offers a sampling of zero trust use cases; outlines five core principles; and lists five implementation stages.
“Zero Trust is designed to protect organizations from cyberattacks, but the journey towards Zero Trust is long and rarely aligned with the traditional cybersecurity strategies to which we have grown accustomed,” the blog reads.

For more information about zero trust:
- “Zero Trust Maturity Model – Version 2.0” (CISA)
- “What is zero trust? A model for more effective security” (CSO)
- “7 steps for implementing zero trust, with real-life examples” (TechTarget)
- “5 Best Practices from Industry for Implementing a Zero Trust Architecture” (Carnegie Mellon University)
VIDEOS
Ultimate Guide to Zero Trust for Businesses (TechTarget)
- Cloud
- Cybersecurity Snapshot
- Exposure Management
- Risk-based Vulnerability Management


