Surge of Attacks Targeting Network Infrastructure Devices – What You Need to Know

Based on the recent surge of attacks on network devices by Russian state-sponsored cyber actors, the US-CERT has released Technical Alert (TA18-106A). As of now, targets are primarily government and private-sector organizations, critical infrastructure providers and the internet service providers (ISPs) that support U.S. infrastructure. Tenable has warned about such attacks before, including as recently as last week.
Impact assessment
Network devices are ideal targets because all traffic must traverse these critical devices. Organizations that use legacy, unencrypted protocols to manage hosts and services make successful credential harvesting easy for cyber actors. An attacker who has gained access to an organization’s gateway router can monitor, modify and deny traffic to and from the device. Simply put, whoever controls the router controls the data flowing through it.
According to the US CERT, Russian state-sponsored cyber actors have conducted both broad-scale and targeted scanning of internet address spaces. Broad scanning helps attackers identify enabled internet-facing ports and services, conduct device fingerprinting and discover vulnerable network infrastructure devices. Vulnerable protocols targeted in this scanning include:
- Telnet (port 23)
- HTTP (port 80)
- SNMP (port 161/162)
- SMI (port 4786)
However, an attacker who gains control of a router between Industrial Control Systems – Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (ICS-SCADA) sensors and the controllers in a critical infrastructure, such as the energy sector, can manipulate the messages, creating dangerous configurations that could lead to loss of service or physical destruction.
Vulnerability details
For several years now, cyber actors have been targeting and exploiting enterprise-class and SOHO/residential routers and switches worldwide. Many times, cyber actors do not need to leverage zero-day vulnerabilities or install malicious software to exploit these devices. Instead, these cyber actors rely on legacy, weak protocols and services associated with network administrative activities.
Network devices like routers and switches are often easy targets because they’re typically not maintained to the same standard as other devices, such as desktops and servers. Many times, default accounts and passwords are not changed, firmware is not updated and devices are not hardened. Devices such as SOHO and residential routers are most vulnerable. Once compromised, they can be used to pivot to other devices.
These weak security practices may enable cyber actors to:
- Identify vulnerable devices
- Extract device configurations
- Map internal network architectures
- Harvest login credentials
- Masquerade as privileged users
Additionally, cyber actors may be able to modify device firmware, operating systems and configurations as well as copy, modify, deny or redirect traffic. Often, these cyber actors are successful because the devices:
- Have legacy unencrypted protocols or unauthenticated services running
- Have not been sufficiently hardened or are no longer supported (EOL)
- Have not been updated or patched
All these factors give cyber actors the ability to potentially gain both intermittent and persistent access to critical infrastructure.
Exploitation
In many cases, exploitation begins with a brute force attack against Telnet and SSH to obtain login credentials. Weak and commonly used passwords or passwords that have previously been harvested by illicit activities are used for exploitation. However, if default accounts exist, credentials can be easily obtained, which will give full access to these devices. Password hashes may also be extracted from configurations via Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and Cisco Smart Install (SMI) enabled device scanning.
Urgently required actions
Tenable suggests analyzing the network to determine whether any of the specific services listed below are running and/or ports are open. Refer to the vendor-specific guidance for the make and model of network devices in operation.
The US-CERT recommends that all organizations take the following actions:
- Do not allow unencrypted (i.e., plain text) management protocols (e.g., Telnet) to enter an organization from the internet. When encrypted protocols such as SSH, HTTPS or TLS are not possible, management activities from outside the organization should be done through an encrypted VPN where both ends are mutually authenticated.
- Do not allow internet access to the management interface of any network device. The best practice is to block internet-sourced access to the device management interface and restrict device management to an internal trusted and whitelisted host or LAN. If access to the management interface cannot be restricted to an internal trusted network, restrict remote management access via encrypted VPN capability where both ends are mutually authenticated. Whitelist the network or host from which the VPN connection is allowed, and deny all others.
- Disable legacy unencrypted protocols such as Telnet and SNMPv1 or v2c. Where possible, use modern encrypted protocols such as SSH and SNMPv3. Harden the encrypted protocols based on current best security practices. DHS strongly advises owners and operators to retire and replace legacy devices that cannot be configured to use SNMPv3.
- Immediately change default passwords and enforce a strong password policy. Do not reuse the same password across multiple devices. Each device should have a unique password. Where possible, avoid legacy password-based authentication, and implement two-factor authentication based on public-private keys. See NCCIC/US-CERT TA13-175A – Risks of Default Passwords on the Internet, last revised October 7, 2016.
Further detailed information can be found in the ‘Solution’ and ‘General Mitigation’ section of the US-CERT Alert (TA18-106A).
Identifying affected systems
Tenable has pre-existing detection via these Nessus plugins:
Tenable has developed the following Nessus plugins specifically for detection of Cisco routers:
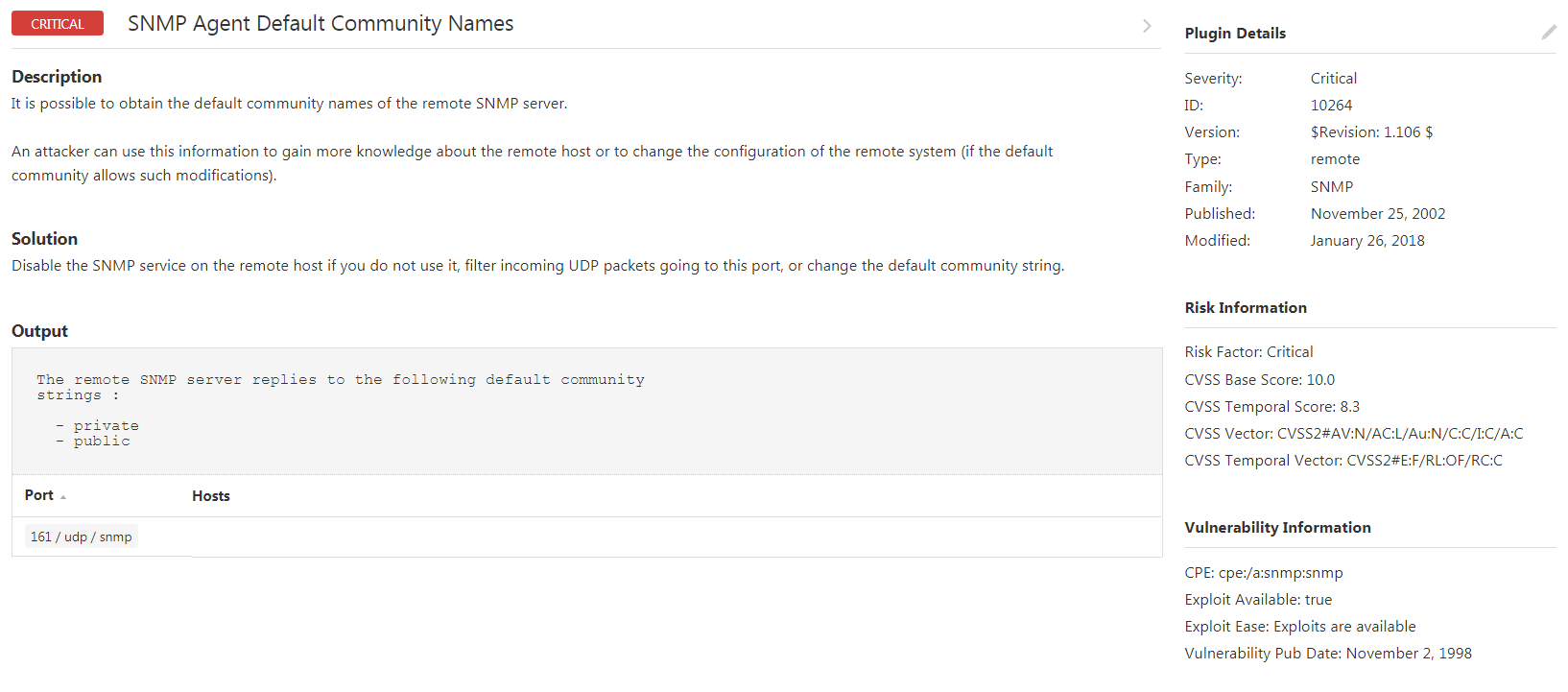
10264 SNMP Agent Default Community Names – It is possible to obtain the default community names of the remote SNMP server. An attacker can use this information to gain more knowledge about the remote host or change the configuration of the remote system (if the default community allows such modifications).
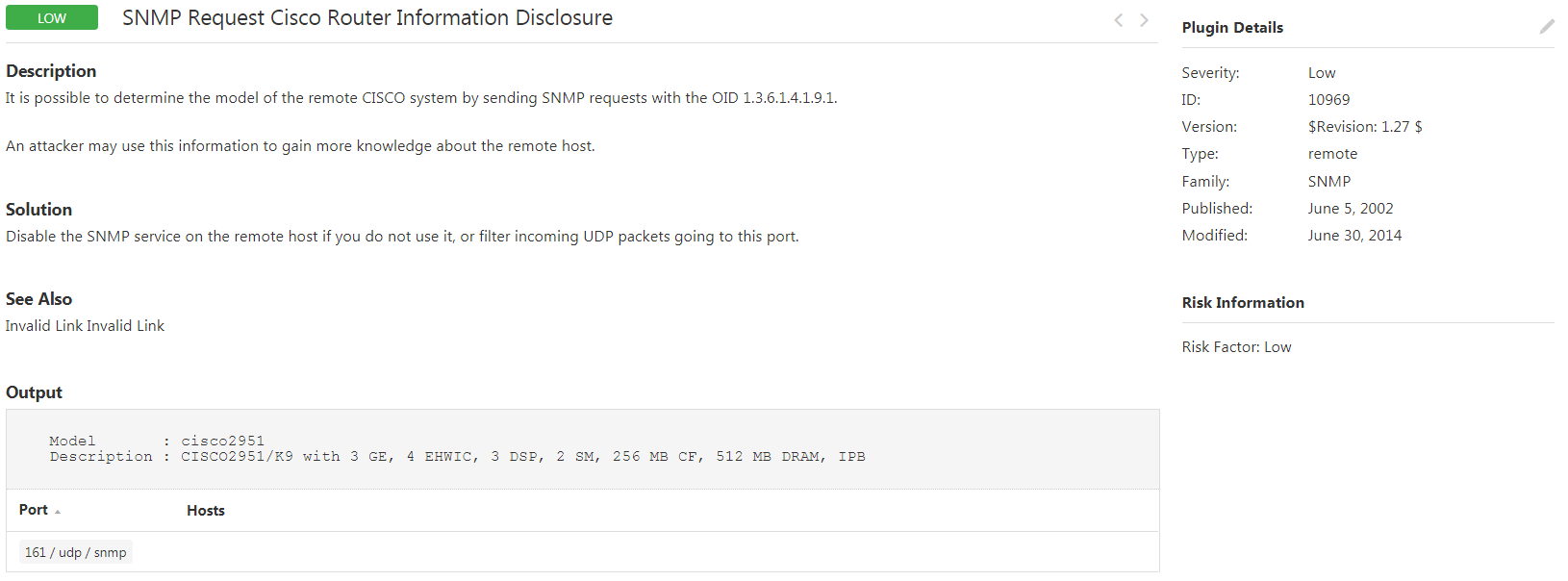
10969 SNMP Request Cisco Router Information Disclosure – It is possible to determine the model of the remote Cisco system by sending SNMP requests with the OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.1. An attacker may use this information to gain more knowledge about the remote host.
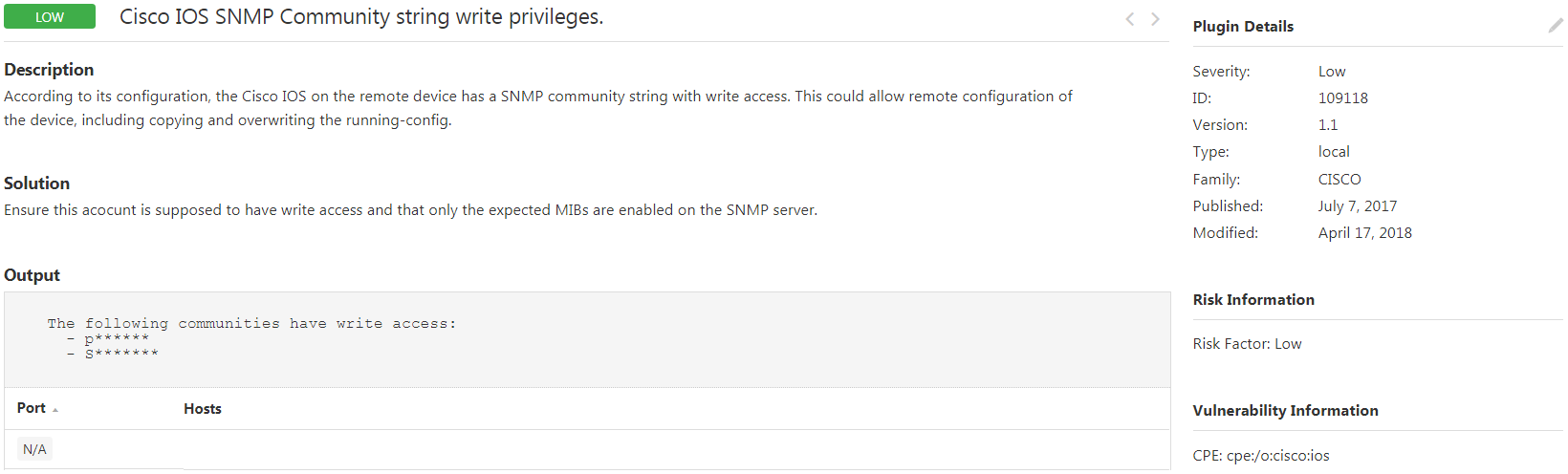
109118 Cisco IOS SNMP Community String Write Privileges – According to its configuration, the Cisco IOS on the remote device has an SNMP community string with write access. This could allow remote configuration of the device, including copying and overwriting the running-config.
Get more information
- US-CERT Alert (TA18-106A)
- Cisco Smart Install - How to Prevent Attacks on Switches
- Cisco Smart Install Protocol Misuse
- Learn more about Tenable.io, the first Cyber Exposure platform for holistic management of your modern attack surface
- Get a free 60-day trial of Tenable.io Vulnerability Management
- Plugins


