by John Thounhurst
February 6, 2026
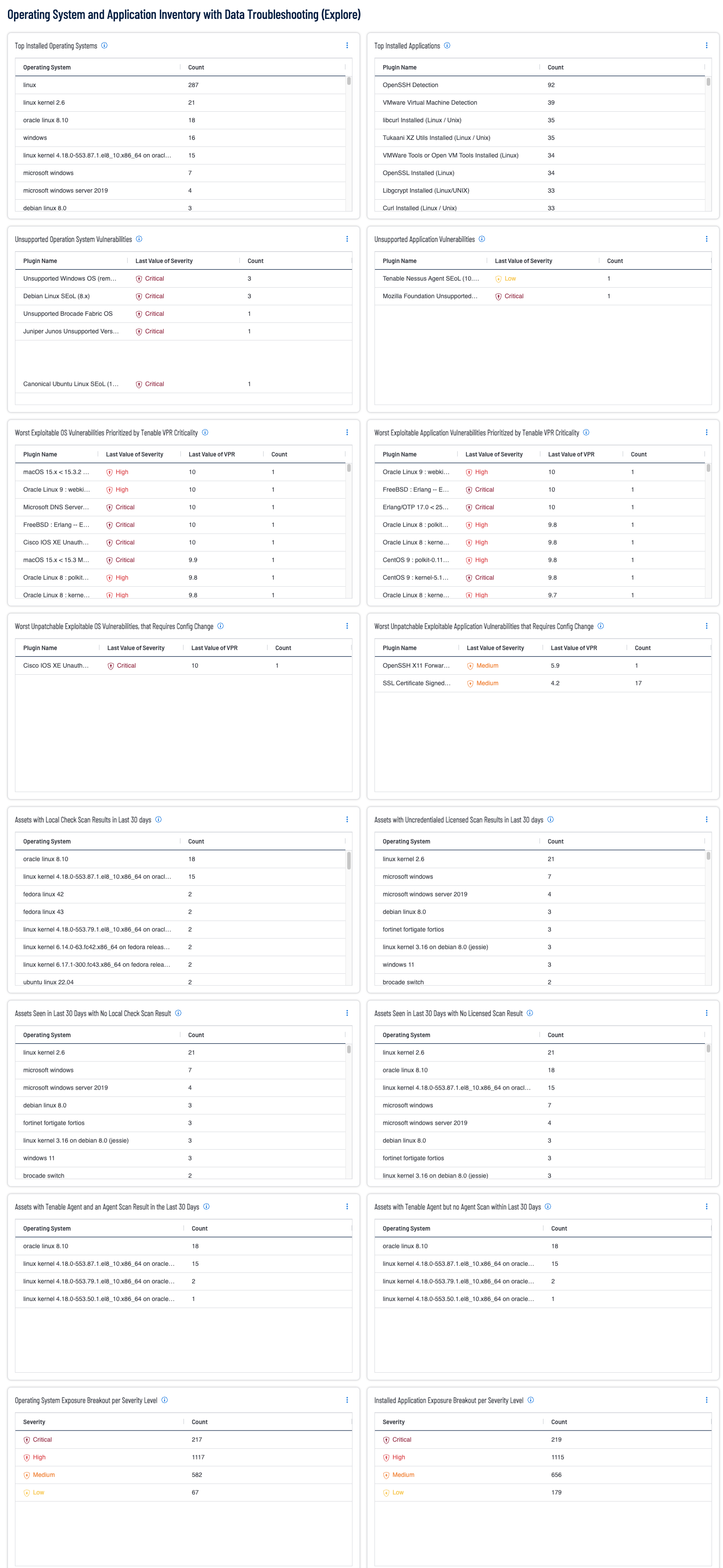
Security practitioners need full visibility of all vulnerabilities within the organization. By leveraging the continuous asset scanning and automated risk prioritization capabilities of Tenable Vulnerability Management (TVM), the practitioner is able to discover operating system and application instances, software vulnerabilities, misconfigurations and other exposure details. This dashboard provides a high-level summary of asset counts per operating system and discovered applications, with the added benefit of helpful queries to identify troublesome areas in scan fidelity.
A key first step in establishing an exposure management program is to separate findings by operating systems and applications. This discovery process helps to assess the technology in the environment and discover gaps in exposure management. The widgets in the dashboard focus on either operating system vulnerabilities or application vulnerabilities by leveraging the CPE (Common Platform Enumeration) strings that are defined by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) and provide a unique, standardized name for IT products. Using this comprehensive approach to data analysis, the risk manager is able to obtain visibility into the network and prioritize mitigation efforts accordingly.
Once the vulnerabilities are known to the risk managers the risk prioritization begins. In cases where a vendor supplied patch is available, patch management solutions are able to increase efficiency by distributing and applying the patches. However, there are many cases where unsupported operating systems or patches have not been released yet. Oftentimes unpatchable vulnerabilities are identified as exploitable, and to remediate the risk requires a configuration change such as a registry key change, disabling insecure or deprecated protocols, and upgrading to a supported operating system version or new operating system.
As the exposure management program matures, the security operations team needs to begin to measure data collection and the remediation processes. To allow for accurate measurements, the fidelity of the scanning program needs to be reviewed and monitored. To assist in this process the dashboard has several widgets that enable the understanding of scan health by identifying gaps in the scan activities. Organizations that utilize both agent scans and network scans are able to benefit from each method and begin to close the gaps in scan coverage. The dashboard helps to show the health of credentialed network scan, also known as an authenticated scan (which provides a deeper insight into the risk posture of the asset), as compared to discovery scanning. If credentialed network scans are not available, the organization can leverage the Tenable Agent to collect vulnerability data. While agents are not designed to perform network checks, certain settings cannot be checked or obtained, therefore combining network scans with agent-based scanning eliminates this gap. The key thing to keep in mind is that scanning with credentials will provide the best and most complete asset info, vulnerability and patch auditing picture with a regular scanning cadence and depth. Local Check Scans with the Tenable Agent or working credentials will provide the more complete and hi-fidelity data set that is needed and ensure the good data passes downstream for reporting, workflows and stakeholders.
Tenable Vulnerability Management provides the ability to Know the vulnerabilities on the network and provides full visibility with continuous asset scanning and automated risk prioritization capabilities. The data on this dashboard helps to Expose gaps and facilitate the process in which the risk manager is able to quickly find highly exploitable, business-impacting vulnerabilities using risk-based threat intelligence and critical asset identification. As the risk mitigations efforts increase their affection, the CISO is able to Close the critical exposures and make rapid, decisive decisions that direct actions to mitigate high-risk vulnerabilities and communicate leadership and stakeholders as the current state of the exposure management program.
Widgets
- Top Installed Operating Systems: The table provides a list of operating systems detected over the last 30 days by using Nessus, Tenable Agent or Nessus Network Monitor. This widget leverages the Operating System exists filter to only display assets with a positive identification of the operating system. In order to facilitate accurate OS identification, the scans will need to be performed using Local Check scans with the Tenable Agent or with valid credentials.
- Top Installed Applications: The table displays the vulnerabilities related to applications last observed over the last 30 days, displays the plugin name and count of found on the network. This widget leverages the CPE (Common Platform Enumeration) filter to identify application related findings.
- Assets with Local Check Scan Results in Last 30 days: This table provides a summary count of assets by operating system that have been scanned using valid elevated credentials or by a Tenable Agent during the last 30 days. These systems have been assessed using the most thorough means possible, and if supported have completed a missing patch assessment. Many systems such as Windows, Linux and Mac OS support detailed assessment, while other systems such as network devices, appliances, or closed systems may use operating system identification to identify vulnerabilities.
- Assets with Uncredentialed Licensed Scan Results in Last 30 days: This table provides a summary count of assets by operating system that have been scanned during the last 30 days in which the asset was considered licensed and counted towards Tenable's license limit. A licensed scan uses non-discovery plugins and can identify vulnerabilities. Unauthenticated scans that run non-discovery plugins update the Last Licensed Scan field, but not the Last Authenticated Scan field.
- Unsupported Operation System Vulnerabilities: The widget displays unsupported operating system vulnerabilities. Knowing which operating systems are unsupported or approaching end-of-life (EOL) can improve a security team's ability to mitigate vulnerabilities and secure the network. Assets running unsupported operating systems are more vulnerable to exploitation.
- Unsupported Application Vulnerabilities: The widget displays unsupported application vulnerabilities. Knowing which applications are unsupported or approaching end-of-life (EOL) can improve a security team's ability to mitigate vulnerabilities and secure the network. Assets running unsupported software are more vulnerable to exploitation.
- Worst Exploitable OS Vulnerabilities Prioritized by Tenable VPR Criticality: This widget displays the worst exploitable OS-based vulnerabilities identified within the organization. The table is sorted using the Vulnerability Priority Rating (VPR) score, which is a scale from range from 0.1 to 10.0, where a higher value represents a higher likelihood of exploitation. These findings are the worst exploitable OS-Based vulnerabilities and require immediate mitigation actions. Prioritizing by Tenable VPR enables the organization to reduce remediation time and keeps operational costs at a minimum by identifying the most significant exposures that are being actively exploited in the wild by cyber criminals.
- Worst Exploitable Application Vulnerabilities Prioritized by Tenable VPR Criticality: This widget displays the worst exploitable application based vulnerabilities identified within the organization. These findings are the worst exploitable application based vulnerabilities and require immediate mitigation actions. Prioritizing by Tenable VPR enables the organization to reduce remediation time and keeps operational costs at a minimum by identifying the most significant exposures that are being actively exploited in the wild by cyber criminals. System configurations and vulnerabilities are best identified throughout the organization and related infrastructure when scanning with Nessus (using valid credentials to perform Local Checks), or when using Tenable Agents.
- Worst Unpatchable Exploitable OS Vulnerabilities, that Requires Config Change: These are the worst exploitable OS vulnerabilities within the environment that are not patchable. Prioritizing by Tenable VPR enables the organization to reduce remediation time and keeps operational costs at a minimum by identifying the most weaponized exposures that are being actively exploited in the wild by cyber criminals. Typically all of these vulnerabilities are very bad, unpatchable exposures require a configuration change to the asset, such as a registry key change, disabling insecure, deprecated protocols or upgrading to a supported OS version or new OS.
- Worst Unpatchable Exploitable Application Vulnerabilities that Requires Config Change: These are the worst exploitable application vulnerabilities within the environment that are not patchable. Prioritizing by Tenable VPR enables the organization to reduce remediation time and keeps operational costs at a minimum by identifying the most weaponized exposures that are being actively exploited in the wild by cyber criminals.
- Assets Seen in Last 30 Days with No Local Check Scan Result: This widget provides a list of assets that are active in the network, as they have been scanned in the last 30 days. However the assets have not been scanned using elevated credentials that enable local checks or by a Tenable Agent (for Windows, Linux and Mac OS assets) in the last 30 days.
- Assets Seen in Last 30 Days with No Licensed Scan Result: The assets in this table are present on the network during the last 30 days, but have not been scanned in a manner that consumes a license. A Licensed Scan is anything beyond a basic Host Discovery Scan (such as a non-Credentialed subnet scan or a Local Check scan with Credentials or the Tenable Agent). Running scans that utilize Local Checks are essential in fully assessing assets for risk and enumerating the installed OS, applications, running services and patching.
- Assets with Tenable Agent and an Agent Scan Result in the Last 30 Days: The assets in this table are identified as having been scanned during the last 30 days with Tenable Agent, which ensures the system is properly assessed to perform all local checks. Tenable Agent scans use lightweight, low-footprint programs that are installed locally on the asset. Tenable Agents collect vulnerability, compliance, and system data, and report that information back to Tenable Vulnerability Management for analysis. Tenable Agents are designed to have minimal impact on the system and the network, giving you the benefit of direct access to all hosts without disrupting your end users.
- Assets with Tenable Agent but no Agent Scan within Last 30 Days: The assets in this table are identified as having been scanned during the last 30 days with Tenable Agents, which ensures the system is properly assessed to perform all local checks. However the Tenable Agent of the asset has not reported into Tenable Vulnerability Management in the last 30 days. This list of assets should be shared with the appropriate operations team to determine if the asset has been removed from service or not.
- Operating System Exposure Breakout per Severity Level: This widget provides a summary count of vulnerabilities detected using the CPE (Common Platform Enumeration) filter to identify operating system related findings. The vulnerabilities identified have been recently observed within the last 30 days.
- Installed Application Exposure Breakout per Severity Level: This widget provides a summary count of vulnerabilities detected using the CPE (Common Platform Enumeration) filter to identify application related findings. The vulnerabilities identified have been recently observed within the last 30 days.